W5100S TCP Function
By setting some Registers and Memory Operation, W5100S provides Internet Connectivity. This Chapter describes How to operate W5100S TCP Function.
Initialization
Basic Setting
For W5100S Operation, select and utilize appropriate Registers shown below.
- Mode Register (MR)
- Interrupt Mask Register (IMR)
- Retry Time-value Register (RTR)
- Retry Count Register (RCR)
For more Information of above Registers, refer to the “Register Descriptions” in W5100S Datasheet.
Setting Network Information
Basic Network Information setting for Communication: It must be set the basic Network Information.
- SHAR(Source Hardware Address Register)
- It is prescribed that the Source Hardware Addresses, which is set by SHAR, use unique Hardware Addresses (Ethernet MAC address) in the Ethernet MAC Layer. The IEEE manages the MAC address allocation. The manufacturer which produces the Network device allocates the MAC Address to product.
- Details on MAC address allocation refer to the website as below.
- 🌎http://www.ieee.org/
- 🌎http://standards.ieee.org/regauth/oui/index.shtml
- GAR(Gateway Address Register)
- SUBR(Subnet Mask Register)
- SIPR(Source IP Address Register)
Set SOCKET n Buffer Information
This stage shows SOCKET n TX/RX Buffer Information. The base Address and Mask Address of each SOCKET are set in this stage.
*In case of, assign 2KB TX/RX Buffer per SOCKET
In case of, assign 2KB TX/RX Buffer per SOCKET
{
// set Base Address of TX/RX Buffer for SOCKET n
gS0_RX_BASE = 0x8000; // TX Buffer Block Base Address
gS0_RX_BASE = 0xC000; // RX Buffer Block Base Address
TxTotalSize = 0; // For check the total size of SOCKET n TX Buffer
RxTotalSize = 0; // For check the total size of SOCKET n RX Buffer
for (n=0; n<3; n++) {
Sn_TXBUF_SIZE = 2; // assign 2KB TX Buffer per SOCKET
Sn_RXBUF_SIZE = 2; // assign 2KB RX Buffer per SOCKET
// 0x07FF, for getting offset address within assigned SOCKET n TX/RX Buffer
gSn_TX_MASK = (1024 * Sn_TXBUF_SIZE) – 1;
gSn_RX_MASK = (1024 * Sn_RXBUF_SIZE) - 1;
if( n != 0) {
gSn_TX_BASE = gSn-1_TX_BASE + (1024 * Sn-1_TXBUF_SIZE);
gSn_RX_BASE = gSn-1_RX_BASE + (1024 * Sn-1_RXBUF_SIZE);
} // end if
TxTotalSize = TxTotalSize + Sn_TXBUF_SIZE;
RxTotalSize = RxTotalSize + Sn_RXBUF_SIZE;
If( TxTotalSize > 8 or RxTotalSize > 8 ) goto ERROR; // invalid Total Size
} // end for
}
Data Communications
After Initialization Process, SOCKET is opened on TCP, UDP, IPRAW or MACRAW Mode and able to transmit and receive Data. This stage shows How to use SOCKET on TCP Mode.
TCP
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is a bidirectional Data Transmission
Protocol based on a 1:1 communication on Transport Layer. It also
provides Communication between Applications by using Port Number. TCP
1:1 communication needs the Connection Process such as transmitting
Connection Request to Peer or receiving Connection Request from Peer. In
this Connection Process, the side transmitting Connection Request is
‘TCP CLIENT’ and the other side receiving Connection Request is ‘TCP
SERVER’. TCP also provides reliable, ordered and error-checked delivery
of a stream Data between applications running on hosts communicating by
an IP network. ‘TCP SERVER’ and ‘TCP CLIENT’ are maintaining transmit
and receive Data until the TCP connection is terminated. 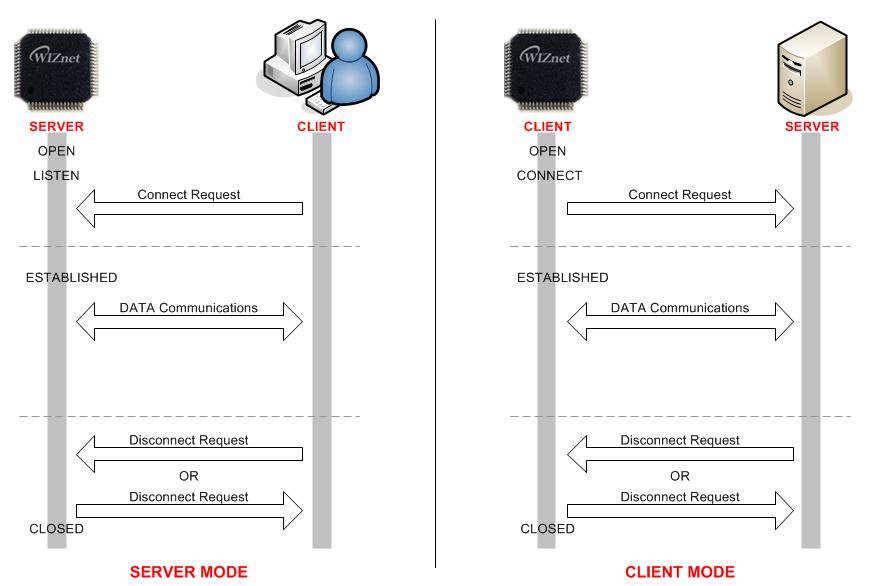
TCP SERVER
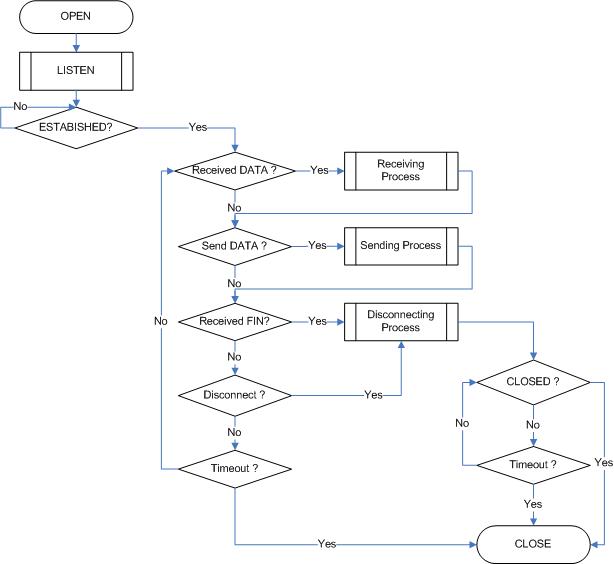
SOCKET Initialization
SOCKET Initialization is required for TCP Mode SOCKET. The Initialization consists of SOCKET Mode setting, SOCKET Port Number setting, SOCKET Option setting and SOCKET OPEN Command. 4 SOCKETs are all opened as TCP Mode. After OPEN Command(Sn_CR = OPEN), if the SOCKET status(Sn_SR) is changed to SOCKET_INIT, SOCKET Initialization is completed. This process is identically applied in "TCP SERVER" and "TCP CLIENT".
{
START:
Sn_MR[3:0] = "0001"; // set TCP Mode
Sn_PORTR0,1 = source_port; // sets source port number
/* configure SOCKET Option when you need it */
// Sn_MR[ND] = '1'; // set No Delay ACK
Sn_CR = OPEN; // sets OPEN command
/* wait until Sn_SR is changed to SOCK_INIT */
if (Sn_SR != SOCK_INIT) Sn_CR = CLOSE; goto START;
}
LISTEN
Run as “TCP SERVER” by LISTEN Command.
{
/* listen SOCKET */
Sn_CR = LISTEN;
/* wait until Sn_SR is changed to SOCK_LISTEN */
if (Sn_SR != SOCK_LISTEN) Sn_CR = CLOSE; goto START;
}
ESTABLISHMENT
"TCP SERVER" keeps Sn_SR (SOCK_LISTEN) until received SYN Packet. If "TCP SERVER" receives SYN Packet from "TCP CLIENT", it transmits SYN/ACK Packet to ‘TCP CLIENT’ and the Connection Process between "TCP SERVER" and "TCP CLIENT" is completed. If there is no response from Peer against of transmitted SYN Packet or SYN/ACK Packet within the Retransmission Time, Sn_IR [TIMEOUT] is set to ‘1’.
First method :
{
/* check SOCKET Interrupt */
if (Sn_IR[CON] == ‘1’)
{
/* clear SOCKET Interrupt */
Sn_IR[CON] = ‘1’;
goto Received DATA?; /* or goto Send DATA?; */
}
else if(Sn_IR[TIMEOUT] == ‘1’) goto Timeout?;
}
Second method :
{
if (Sn_SR == SOCK_ESTABLISHED)
{
/* clear SOCKET Interrupt */
Sn_IR[CON] = ‘1’;
goto Received DATA? /* or goto Send DATA?; */
}
else if(Sn_IR[TIMEOUT] == ‘1’) goto Timeout?;
}
Receive DATA?
Whether SOCKET n Data is received is confirmed by Sn_IR [RECV] or Sn_RX_RSR.
First method :
{
/* check SOCKET RX Memory Received Size */
if (Sn_RX_RSR > 0) goto Receiving Process;
}
Second method :
{
if (Sn_IR[RECV] == ‘1’)
{
/* check SOCKET Interrupt */
Sn_IR[RECV] = ‘1’; /* clear SOCKET Interrupt */
goto Receiving Process;
}
}
LISTEN
Run as “TCP SERVER” by LISTEN Command.
{
/* listen SOCKET */
Sn_CR = LISTEN;
/* wait until Sn_SR is changed to SOCK_LISTEN */
if (Sn_SR != SOCK_LISTEN) Sn_CR = CLOSE; goto START;
}
ESTABLISHMENT
"TCP SERVER" keeps Sn_SR (SOCK_LISTEN) until received SYN Packet. If "TCP SERVER" receives SYN Packet from "TCP CLIENT", it transmits SYN/ACK Packet to ‘TCP CLIENT’ and the Connection Process between "TCP SERVER" and "TCP CLIENT" is completed. If there is no response from Peer against of transmitted SYN Packet or SYN/ACK Packet within the Retransmission Time, Sn_IR [TIMEOUT] is set to ‘1’.
First method :
{
/* check SOCKET Interrupt */
if (Sn_IR[CON] == ‘1’)
{
/* clear SOCKET Interrupt */
Sn_IR[CON] = ‘1’;
goto Received DATA?; /* or goto Send DATA?; */
}
else if(Sn_IR[TIMEOUT] == ‘1’) goto Timeout?;
}
Second method :
{
if (Sn_SR == SOCK_ESTABLISHED)
{
/* clear SOCKET Interrupt */
Sn_IR[CON] = ‘1’;
goto Received DATA? /* or goto Send DATA?; */
}
else if(Sn_IR[TIMEOUT] == ‘1’) goto Timeout?;
}
Receive DATA?
Whether SOCKET n Data is received is confirmed by Sn_IR [RECV] or Sn_RX_RSR.
First method :
{
/* check SOCKET RX Memory Received Size */
if (Sn_RX_RSR > 0) goto Receiving Process;
}
Second method :
{
if (Sn_IR[RECV] == ‘1’)
{
/* check SOCKET Interrupt */
Sn_IR[RECV] = ‘1’; /* clear SOCKET Interrupt */
goto Receiving Process;
}
}
Receiving Process
Received Data is read from SOCKET n RX Buffer Block. The Read Offset Address of Received Data in RX Memory Block is calculated by gSn_RX_BASE, gSn_RX_MASK and Sn_RX_RD. After reading received Data, Sn_RX_RD must be increased by Data read Size and Sn_CR [RECV] must be set to ‘1’. If there is remain Data in SOCKET n RX Buffer Block after Sn_CR [RECV] Command, Sn_IR [RECV] is set to ‘1’. When Read Offset Address calculated, it is cautious to over the boundary Address (n=0,1,2 : gSn_RX_BASE ∼ gSn+1_RX_BASE, n=3 : gS3_RX_BASE ∼ 0xFFFF) of SOCKET n RX Buffer Block.
{
/* get Received Size */
get_size = Sn_RX_RSR;
/* calculate SOCKET n RX Buffer Size & Offset Address */
gSn_RX_MAX = Sn_RXBUF_SIZE * 1024;
get_offset = Sn_RX_RD & gSn_RX_MASK;
/* calculate Read Offset Address */
get_start_address = gSn_RX_BASE + get_offset;
/* if overflow the upper boundary of SOCKET n RX Buffer */
If( (get_offset + get_size) > gSn_RX_MAX )
{
/* copy upper_size bytes of get_start_address to destination_address
- destination_address is user data memory address */
upper_size = gSn_RX_MAX – get_offset;
memcpy(get_start_address, destination_address, upper_size);
destination_address += upper_size;
/* copy the remained size bytes of gSn_RX_BASE to destination_address */
remained_size = get_size – upper_size;
memcpy(gSn_RX_BASE, destination_address, remained_size);
}
else
{
/* copy get_size of get_start_address to destination_address */
memcpy(get_start_address, destination_address, get_size);
}
/* increase Sn_RX_RD as get_size */
Sn_RX_RD += get_size;
/* set RECV Command */
Sn_CR[RECV] = ‘1’;
while(Sn_CR != 0x00); /* wait until RECV Command is cleared*/
}
Send DATA? / Sending Process
Written Data in SOCKET n TX Buffer Block is transmitted. The Write Offset Address in TX Memory Block is calculated by gSn_TX_BASE, gSn_TX_MASK and Sn_TX_WD. And Data to be transmitted from the Write Offset Address is written. After writing Data, Sn_TX_WD must be increased by Data Size and Data is transmitted by Sn_CR [SEND]. Before Sn_IR [SENDOK] = ‘1’, next Data Transmission Process is not executed. After transmitting Data, the time length until Sn_IR[SENDOK] is depending on SOCKET Count, Data Size and Network Traffic. Also Sn_IR [TIMEOUT] could be occurred. When Write Offset Address calculated, it is cautious to over the boundary Address (n=0,1,2 : gSn_TX_BASE ∼ gSn+1_TX_BASE, n=3 : gS3_TX_BASE ∼ 0xC000) of SOCKET n TX Buffer Block. If there is no response from Peer against of transmitted Data Packet within the Retransmission Time, Sn_IR [TIMEOUT] is set to ‘1’.
{
/* calculate SOCKETn TX Buffer Size & Offset Address */
gSn_TX_MAX = Sn_TXBUF_SIZE * 1024;
get_offset = Sn_TX_WR & gSn_TX_MASK;
/* check the max size of DATA(send_size) & Free Size of SOCKETn TX
Buffer(Sn_TX_FSR)*/
if( send_size >gSn_TX_MAX ) send_size = gSn_TX_MAX;
while(send <= Sn_TX_FSR); // Wait until SOCKET n TX Buffer is free */
/* If you don’t want to wait TX Buffer Free
send_size = Sn_TX_FSR; // write Data as size of Free Buffer */
/* calculate Write Offset Address */
get_start_address = gSn_TX_BASE + get_offset;
/* if overflow the upper boundary of SOCKET n TX Buffer */
If( (get_offset + send_size) > gSn_TX_MAX )
{
/* copy upper size bytes of source_address to get_start_address
- source_address is the start address of user data */
upper_size = gSn_TX_MAX – get_offset;
memcpy(source_address, get_start_address, upper_size);
/* copy the Remained Size Bytes of source_address to gSn_TX_BASE */
source_address += upper_size;
remained_size = send_size – upper_size;
memcpy(source_address, gSn_TX_BASE, remained_size);
}
else
{
/* copy send_size bytes of source_address to get_start_address
- source_address is the start address of user data */
memcpy(source_address, get_start_address, send_size);
}
/* increase Sn_TX_WR as send_size */
Sn_TX_WR += send_size;
/* set SEND Command */
Sn_CR = SEND;
while(Sn_CR != 0x00); /* wait until SEND Command is cleared*/
/* wait until SEND Command is completed or TIMEOUT Interrupt is occurred*/
while(Sn_IR[SENDOK] == ‘0’ and Sn_IR[TIMEOUT] = ‘0’);
/* clear SOCKET Interrupt*/
if(Sn_IR[SENDOK] == ‘1’) Sn_IR[SENDOK] = ‘1’;
else goto Timeout?;
}
Received FIN (Passive Close)
When FIN Packet received from Peer.
First Method:
{
If(Sn_SR == SOCK_CLOSE_WAIT) goto Disconnecting Process;
}
Second Method:
{
If(Sn_IR[DISCON] == ‘1’) goto Disconnecting Process;
}
Disconnected (Active Close)
When FIN Packet transmitted to Peer.
{
/* send FIN Packet */
Sn_CR[DISCON] = ‘1’;
while(Sn_CR != 0x00); /* wait until DISCON Command is cleared*/
goto Disconnecting Process;
}
Disconnecting Process
In Passive Close, if FIN Packet is received from Peer and there is no Data to be transmitted, SOCKET transmits FIN Packet and it will be closed. If there is no response from Peer against of transmitted FIN Packet within the Retransmission Time, Sn_IR [TIMEOUT] is set to ‘1’. In Active Close, if SOCKET transmits FIN Packet to Peer, SOCKET waits for Peer FIN Packet. SOCKET will be closed after receiving FIN Packet from Peer. If there is no response from Peer against of transmitted FIN Packet within the Retransmission Time, Sn_IR [TIMEOUT] is set to ‘1’.
Passive Close: /* received FIN Packet from Peer */
{
/* send FIN Packet */
Sn_CR = DISCON;
while(Sn_CR != 0x00); /* wait until DISCON Command is cleared*/
/* wait unit ACK Packet is received*/
while(Sn_IR[DISCON] == ‘0’ and Sn_IR[TIMEOUT] == ‘0’) ;
if (Sn_IR[DISCON] == ‘1’)
{
/* clear Interrupt */
Sn_IR[DISCON] = ‘1’;
goto CLOSED;
}
else goto Timeout?;
}
Active Close : /* sent FIN Packet to Peer */
{
/* wait until FIN Packet is received*/
while(Sn_IR[DISCON] == ‘0’ and Sn_IR[TIMEOUT] == ‘0’) ;
if (Sn_IR[DISOCN] == ‘1’)
{
/* clear Interrupt */
Sn_IR[DISCON] = ‘1’;
goto CLOSED;
}
else goto Timeout?;
}
Timeout?
If there is no response from Peer against of transmitted SYN or SYN/ACK or FIN or Data Packet within the Retransmission Time, Sn_IR [TIMEOUT] is set to ‘1’.
{
/* check TIMEOUT Interrupt */
if(Sn_IR[TIMEOUT] == ‘1’)
{
/* clear Interrupt */
Sn_IR[TIMEOUT] = ‘1’;
goto CLOSE;
}
}
CLOSE
SOCKET n is closed by the Disconnect Process, Sn_IR[TIMEOUT] = '1' and Sn_CR[CLOSE] = '1'.
{
/*wait until SOCKET n is closed*/
while(Sn_SR != SOCK_CLOSED);
}
TCP CLIENT
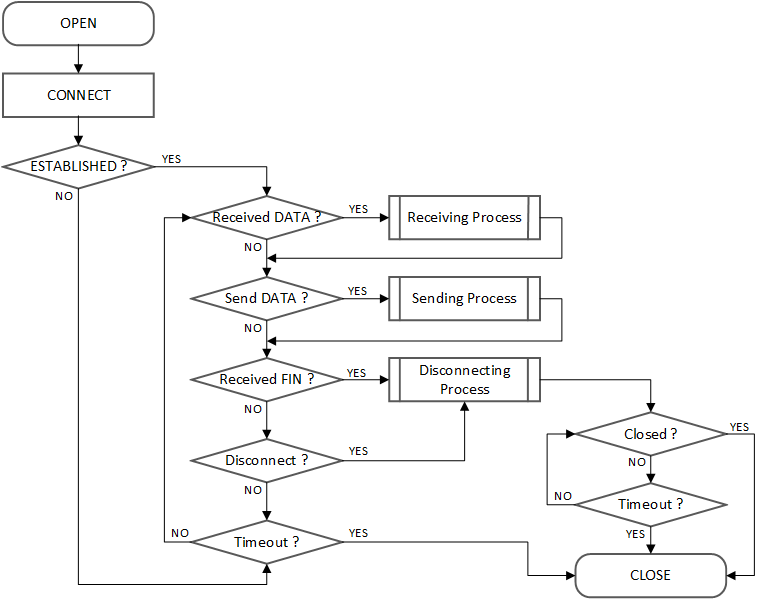
OPEN
It is the same as "TCP SERVER".
CONNECT
SOCKET n is operated as "TCP CLIENT" by Sn_CR[CONNECT]. SYN Packet is transmitted to "TCP SERVER" by Sn_CR[CONNECT].
{
/* set Destination IP Address, 192.168.0.11 */
Sn_DIPR[0:3] ={ 0xC0, 0xA8, 0x00, 0x0B};
/* set Destination PORT Number, 5000(0x1388) */
Sn_DPORTR[0:1] = {0x13, 0x88};
/* set CONNECT Command */
Sn_CR = CONNECT;
while(Sn_CR != 0x00); /* wait until CONNECT Command is cleared*/
goto ESTABLISHED?;
}
ESTABLISHED?
"TCP CLIENT" is in Sn_SR (SOCK_SYNSENT) until receiving SYN/ACK Packet from "TCP SERVER" against of SYN Packet transmitted. If SYN/ACK Packet is received from ‘TCP SERVER’, the Connection Process between ‘TCP SERVER’ and ‘TCP CLIENT’ is completed. If there is no response from Peer against of transmitted SYN Packet within the Retransmission Time, Sn_IR [TIMEOUT] is set to ‘1’.
Others flow
Refer to "TCP SERVER" flow.